
Top Universities in Australia to Study Cyber Security

Cyber security has become one of the most critical pillars of the digital world—protecting everything from personal data and online banking to national infrastructure and global networks. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and scale, the demand for skilled professionals who can defend, detect, and respond to digital risks has never been greater. For students interested in becoming part of this essential frontline, studying cyber security in Australia offers world-class education and global career relevance.
Australia’s top universities deliver cyber security programs that combine deep technical knowledge with practical, hands-on learning. Students explore key areas such as network security, ethical hacking, cryptography, risk management, and digital forensics, while also building crucial skills in problem-solving, incident response, and secure system design. These programs are designed to reflect real-world threats and teach students how to think like defenders—and attackers.
What sets Australia apart is its close alignment between academia and industry. Many universities work in partnership with government agencies, tech companies, and security labs to offer internships, certifications, and real-time threat simulation environments. Whether you’re interested in protecting critical infrastructure, working in national intelligence, or developing security solutions for the private sector, Australia’s cyber security programs provide the foundation and connections to launch your career with confidence.
To help you make an informed choice, we’ve compiled a selection of Australia’s top-ranked universities for cyber security—based on academic performance, industry engagement, and their standing in the QS World University Rankings by Subject 2025. These institutions offer the expertise, resources, and industry links needed to thrive in this fast-moving field and build a secure digital future.
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber security is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and digital assets from malicious attacks, data breaches, and unauthorised access. It involves a broad set of strategies, technologies, and processes that secure both personal and organisational information from constantly evolving cyber threats.
Due to technology advancement at a rapid pace, cyber threats evolve consistently and cybersecurity practices will require adaptation to address new challenges, such as those posed by emerging technologies and sophisticated threat actors.
As businesses and governments become more digital, cyber security plays a critical role in maintaining trust, operational resilience, and data privacy. Below we highlight some of the key focus areas which are crucial in the industry.
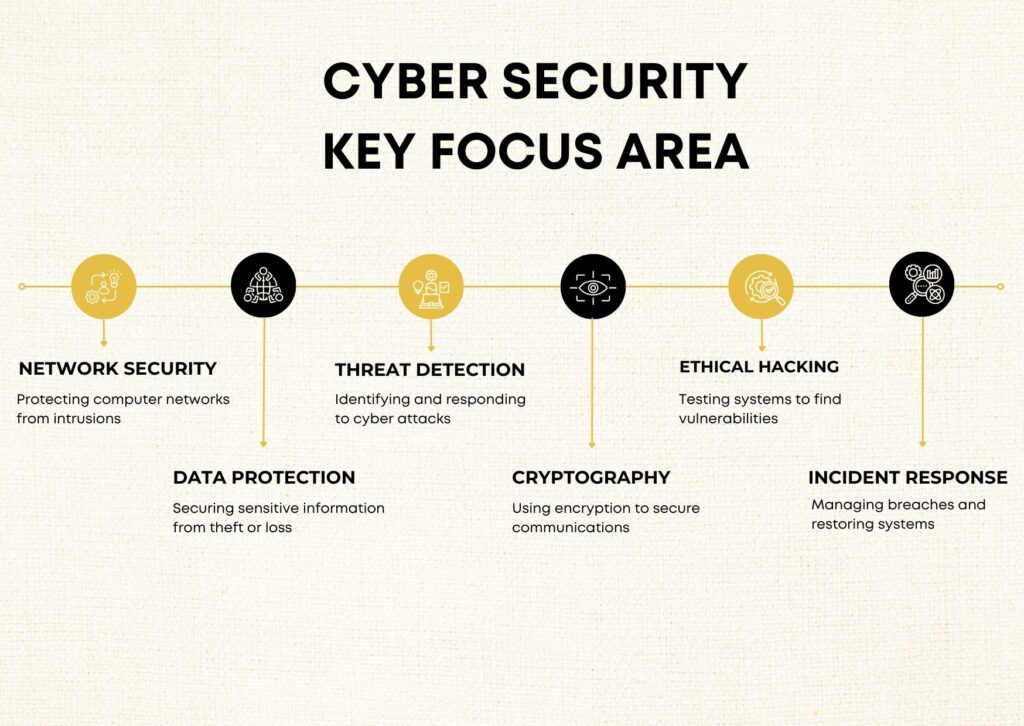
Key Focus Areas:
- Network Security: Protecting computer networks from intrusions
- Data Protection: Securing sensitive information from theft or loss
- Threat Detection: Identifying and responding to cyber attacks
- Cryptography: Using encryption to secure communications
- Ethical Hacking: Testing systems to find vulnerabilities
- Incident Response: Managing breaches and restoring systems
Career Options in Cyber Security
With the rapid rise of digital transformation, cloud computing, and cybercrime, the demand for cyber security professionals has never been higher.
Across industries which include finance, healthcare, government, and tech organisations are facing a growing need to protect sensitive data and digital infrastructure. This talent shortage has created a global surge in job opportunities, with cyber security roles seeing some of the fastest growth in the tech sector.
In 2025 and Australia alone, the demand for cyber security professionals is expected to grow by over 20% in the next 5 years. Globally, the gap between open positions and qualified professionals continues to widen, making it a future-proof and high-paying career path.
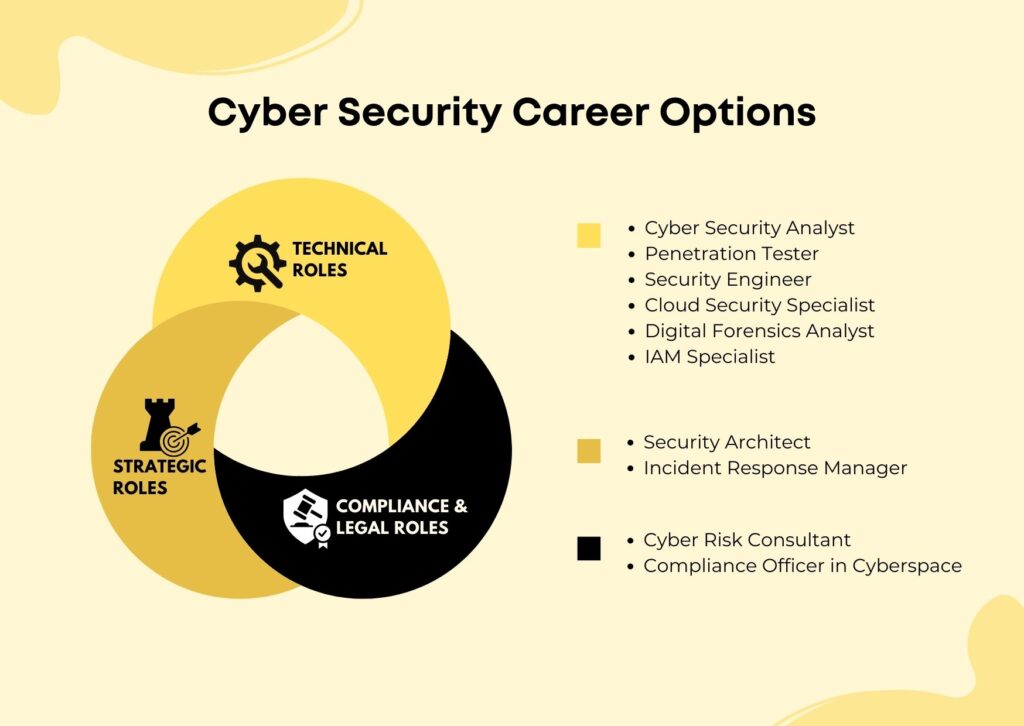
Career Options for Cyber Security Specialist
Technical Roles
- Cyber Security Analyst: Detects and responds to cyber threats.
- Penetration Tester: Finds and exploits system weaknesses ethically.
- Security Engineer: Builds and maintains secure systems.
- Cloud Security Specialist: Protects data on cloud platforms.
- Digital Forensics Analyst: Investigates cyber incidents and recovers data.
- IAM Specialist: Manages user access and authentication.
Strategic Roles
- Security Architect: Designs high-level security infrastructure.
- Incident Response Manager: Leads response to breaches and attacks.
Compliance & Legal Roles
- Cyber Risk Consultant: Assesses risks and advises on mitigation.
- Compliance Officer in Cyberspace: Ensures legal and regulatory cybersecurity standards are met.
How to Become a Cyber Security Specialist?
Cybersecurity specialists play a critical role in protecting organizations from evolving digital threats. Entering this exciting field requires specialized knowledge, practical experience, and continuous skill development.
By following these structured steps highlighted in the examples below: building foundational knowledge, gaining hands-on experience, and continuously expanding your expertise. You’ll unlock pathways to diverse roles like Security Analyst, Penetration Tester, and Cyber Security Engineer.
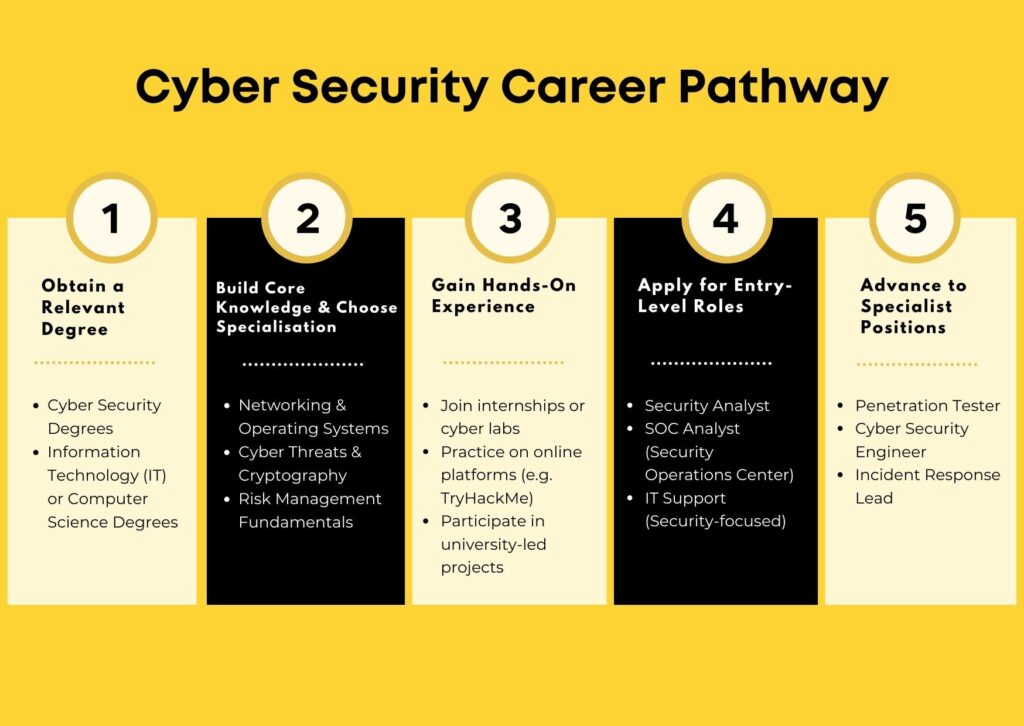
Step 1: Obtain a Relevant Degree
- Cyber Security Degrees
- Information Technology (IT) or Computer Science Degrees
Step 2: Build Core Knowledge and Choosing a Specialisation
- Networking & Operating Systems
- Cyber Threats & Cryptography
- Risk Management Fundamentals
Step 3: Gain Hands-On Experience
- Be involve in Internships or lab experiences
- Register with online training platforms
- Join university or organised cybersecurity projects
Step 4: Apply for Entry-Level Roles
- Security Analyst
Monitors systems for threats, analyses logs, and responds to incidents. Increasingly uses AI-powered tools to detect anomalies and automate threat alerts. - SOC Analyst (Security Operations Center)
Works in real-time monitoring centres to identify, assess, and escalate threats. AI assists in filtering alerts and prioritising critical incidents faster. - IT Support (Security-focused)
Provides frontline assistance for secure system use, password issues, and endpoint protection. May work with AI-driven helpdesk tools or automated security responses.
Step 5: Advance to Specialist Positions
- Penetration Tester: Simulates cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities. AI tools are now used to simulate advanced persistent threats and automate some attack techniques for testing.
- Cyber Security Engineer: Designs and implements secure systems, firewalls, and encryption protocols. Often integrates AI into security architecture to enhance real-time detection and adaptive defence.
- Incident Response Lead: Coordinates the team during security breaches and investigates root causes. Uses AI-based forensics and behavioural analytics to trace attack origins and minimise damage.
Top Recommended University to Study Cyber Security in Australia
Australia is emerging as a global leader in cyber security education, offering cutting-edge programs designed to tackle today’s most complex digital threats. Whether you aim to secure critical infrastructure, combat cybercrime, or build the next generation of secure systems, choosing the right university is your first step.
Explore our top recommendations to discover institutions across Australia that combine world-class teaching, advanced labs, and strong industry partnerships to prepare you for success in this vital and fast-growing field. Your pathway to a career in cyber defence starts here.
The University of Sydney (USYD)

As one of Australia’s oldest and most prestigious institutions, the University of Sydney is globally respected for its academic strength, research innovation, and interdisciplinary approach to solving complex global issues. Consistently ranked among the world’s top universities, it offers students an intellectually dynamic environment in a thriving, future-focused city. For those interested in protecting the digital world, the university’s cyber security offerings blend technical depth with ethical awareness—empowering students to address emerging threats across networks, data systems, and digital infrastructure.
At Sydney, cyber security is not just about defending systems, but understanding the architecture, behaviours, and vulnerabilities that shape them. Students engage with areas such as network security, ethical hacking, cryptography, cyber law, and incident response, all while learning how to analyse risks and design robust, secure systems. With project-based coursework and scenario-based simulations, students develop the critical thinking, adaptability, and hands-on skills essential to navigate today’s digital threat landscape.
The university’s close ties with industry, government, and research centres ensure students have opportunities to apply their learning through internships, live cyber projects, and access to state-of-the-art cyber labs. Whether aiming to work in national security, corporate defence, or digital forensics, students leave prepared to face the evolving challenges of a connected world. Studying cyber security at the University of Sydney provides not only academic excellence, but also a clear pathway into one of the world’s most essential and fast-moving fields.
QS Rankings by Subject in 2025 | #1 in Australia, #36 in the World |
Program | Bachelor of Advanced Computing (Cybersecurity) |
Intake | February, August |
Fees (indicative in 2025) | AUD$57,700 per-year |
Duration | 4 years |
For more information on the table presented above, contact us now!
Australian National University (ANU)

Located in the heart of Canberra, the Australian National University (ANU) stands out as Australia’s national university and a globally respected institution for academic and research excellence. Known for its focus on solving real-world challenges through multidisciplinary study, ANU provides a rigorous and forward-thinking environment—especially well-suited for students seeking to make an impact in the digital security space.
While studying cyber security at ANU, students gain more than just technical training—they develop a strategic mindset for navigating modern digital risks. Core areas of study include network defence, cryptography, secure software systems, and cyber risk analysis, supported by electives that explore the legal, ethical, and social dimensions of cybersecurity. The program equips students with the ability to detect vulnerabilities, respond to incidents, and design secure digital frameworks across a range of sectors.
What makes ANU especially compelling is its access to world-class research infrastructure and government-connected networks. With resources like the National Computational Infrastructure (NCI) and proximity to federal agencies and national security organisations, students benefit from unique exposure to high-level projects and real-time policy relevance. Combined with strong industry partnerships and an emphasis on critical thinking, ANU prepares graduates to take on leadership roles in protecting digital systems at both national and global scales.
QS Rankings by Subject in 2025 | #2 in Australia, #37 in the World |
Program | Bachelor of Computing (Cyber Security) |
Intake | February, July |
Fees (indicative in 2025) | AUD$53,700 per-year |
Duration | 3 years |
For more information on the table presented above, contact us now!
University of Technology Sydney (UTS)
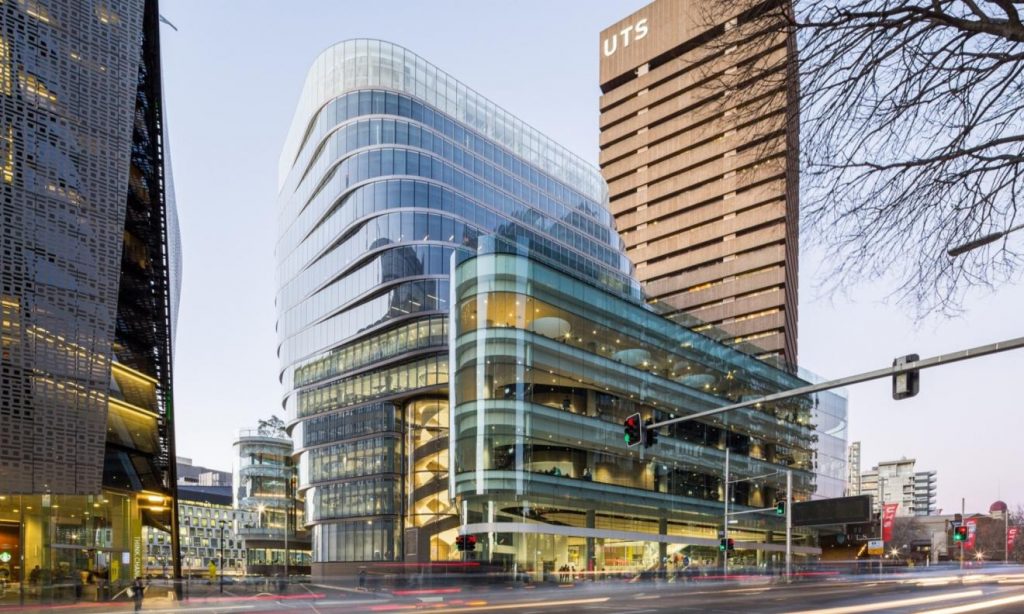

Positioned in Sydney’s leading tech and innovation precinct, the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) is widely recognised for its hands-on learning approach and close industry integration. Known for producing job-ready graduates, UTS offers a practical and future-focused pathway for students aiming to enter the fast-growing field of cyber security.
UTS’s cybersecurity programs emphasise both the technical and strategic aspects of digital defence. Students explore key areas such as ethical hacking, penetration testing, information security management, cryptography, and network protection, while also examining the broader context of cyber law and digital ethics. The curriculum is built around real-world application, encouraging students to work on simulated cyber incidents, case studies, and industry-driven challenges.
What sets UTS apart is its strong connection to Australia’s cyber ecosystem. Through industry projects, internships, and access to specialised security labs, students are immersed in environments where classroom learning translates directly into professional practice. With Sydney’s growing demand for cyber talent, UTS equips graduates with the technical confidence, critical thinking, and situational awareness to protect systems and lead in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
QS Rankings by Subject in 2025 | #6 in Australia, #62 in the World |
Program | Bachelor of Cybersecurity |
Intake | February, July |
Fees (indicative in 2025) | AUD$52,410 per-year |
Duration | 3 years |
For more information on the table presented above, contact us now!
Macquarie University
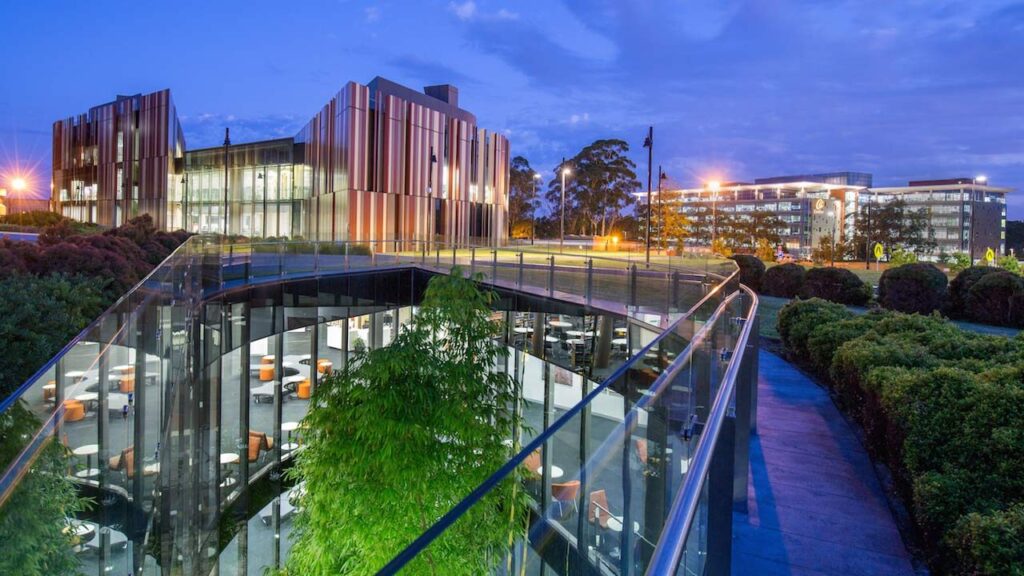

Macquarie University, ranked among the top 200 globally, is recognized as one of Australia’s leading institutions, known for producing highly employable graduates through a blend of academic excellence and industry partnerships.
With state-of-the-art facilities and a future-focused curriculum, Macquarie offers robust programs in cyber security, equipping students with practical experience and technical skills essential for thriving in the competitive global landscape.
The Bachelor of Cybersecurity program at Macquarie provides comprehensive training in areas such as information security, data privacy, digital forensics, applied cryptography, and secure coding.
Beyond technical proficiency, the curriculum emphasizes understanding cybercriminal behaviors and developing strategies to mitigate cyber threats. This holistic approach ensures graduates are prepared for roles like security consultant, risk analyst, and ethical hacker.
Macquarie’s commitment to practical learning is evident through its $10 million investment in the Cyber Security Hub, offering students access to cutting-edge resources and opportunities for real-world engagement. This integration of theoretical knowledge with practical application positions graduates to effectively address complex cybersecurity challenges in various sectors.
QS Rankings by Subject in 2025 | #9 in Australia, #156 in the World |
Program | Bachelor of Cybersecurity |
Intake | February, July |
Fees (indicative in 2025) | AUD$44,500 per-year |
Duration | 3 years |
For more information on the table presented above, contact us now!
Western Sydney University
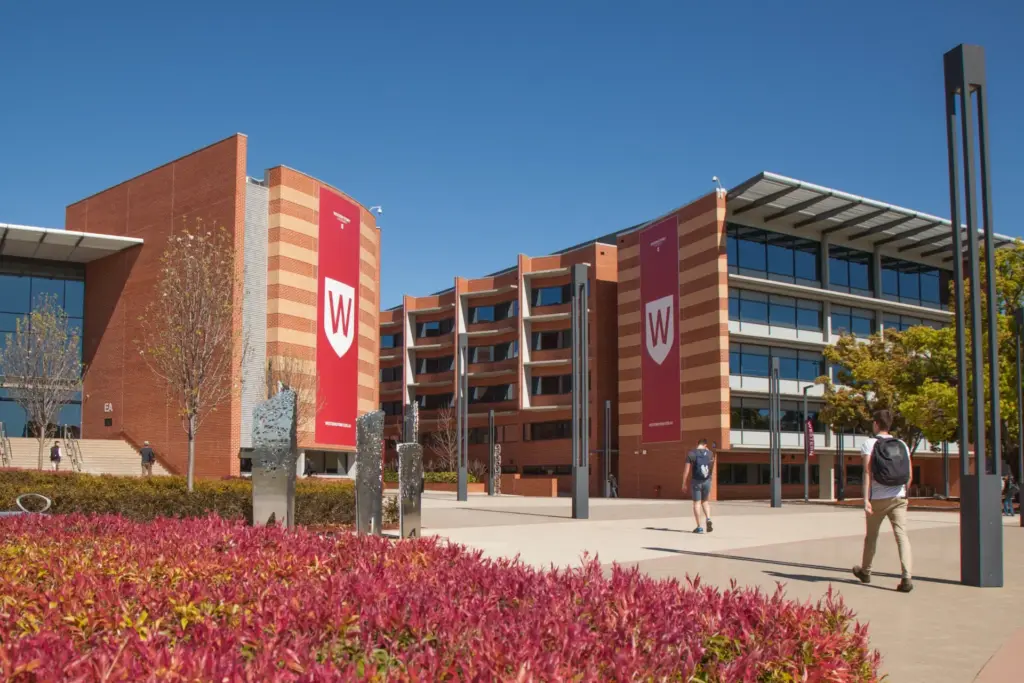

Located in Greater Western Sydney—one of Australia’s fastest-growing economic and innovation corridors—Western Sydney University (WSU) is a forward-thinking institution known for its commitment to real-world learning and interdisciplinary education. With a strong focus on industry collaboration and social impact, WSU offers students a unique opportunity to study cyber security in a setting that blends technical expertise with an understanding of human behaviour.
WSU’s Bachelor of Cyber Security and Behaviour stands out for its integrated approach. The program combines core cyber security training—such as network defence, penetration testing, programming, and cyber risk management—with psychological insights into decision-making, social engineering, and cybercrime. Students learn not only how systems are breached, but why people make the choices that lead to security vulnerabilities.
Practical learning is a cornerstone of the degree. Students gain hands-on experience through placements at the Western Centre for Cybersecurity Aid & Community Engagement and work on real-world security challenges faced by local organisations. With access to industry-led projects and partnerships with key players like Gridware and the E-Safety Commission, WSU prepares graduates for dynamic roles in digital forensics, cyber intelligence, and security architecture. For students seeking a well-rounded cyber security education that reflects the realities of both tech and human factors, WSU offers a uniquely future-ready pathway.
Program | Bachelor of Cyber Security and Behaviour |
Intake | March, July |
Fees (indicative in 2025) | AUD$30,952 per-year |
Duration | 3 years |
For more information on the table presented above, contact us now!
Recommended Articles to Read
Contact us to find out more!
Our consultation service centres are located in various locations in Asia and Oceania including Australia, China, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Fiji and many more. However, if you have a direct enquiry, you can contact us through:
Call/ WhatsApp: +60162206607
Email: [email protected]
About the Author

Sasvin Ravi
I am a freelance content writer, writing on a weekly basis while discovering my true passion..

